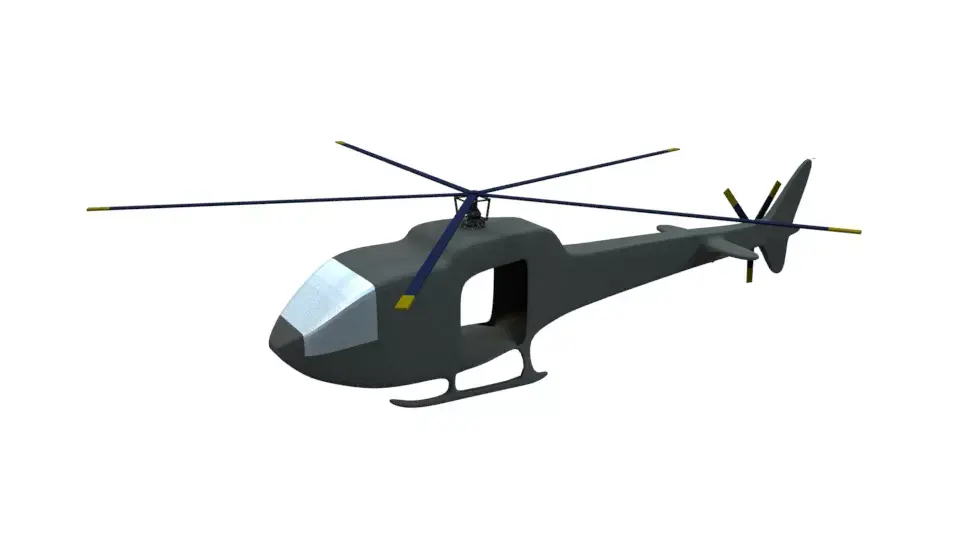
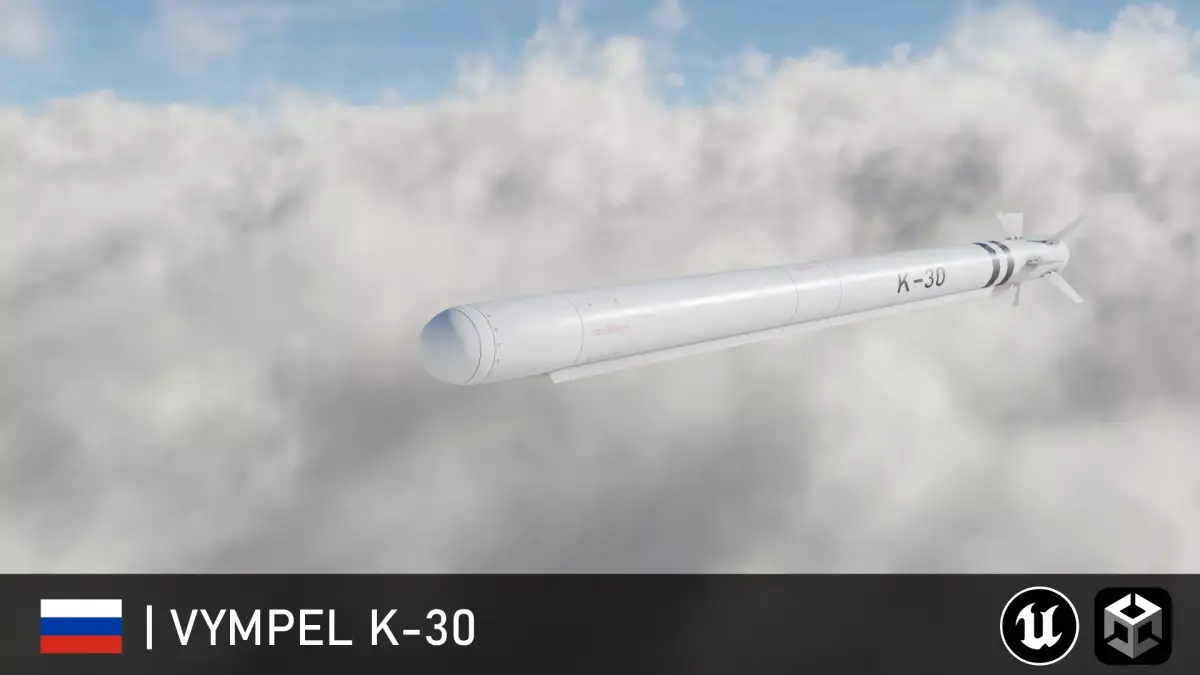
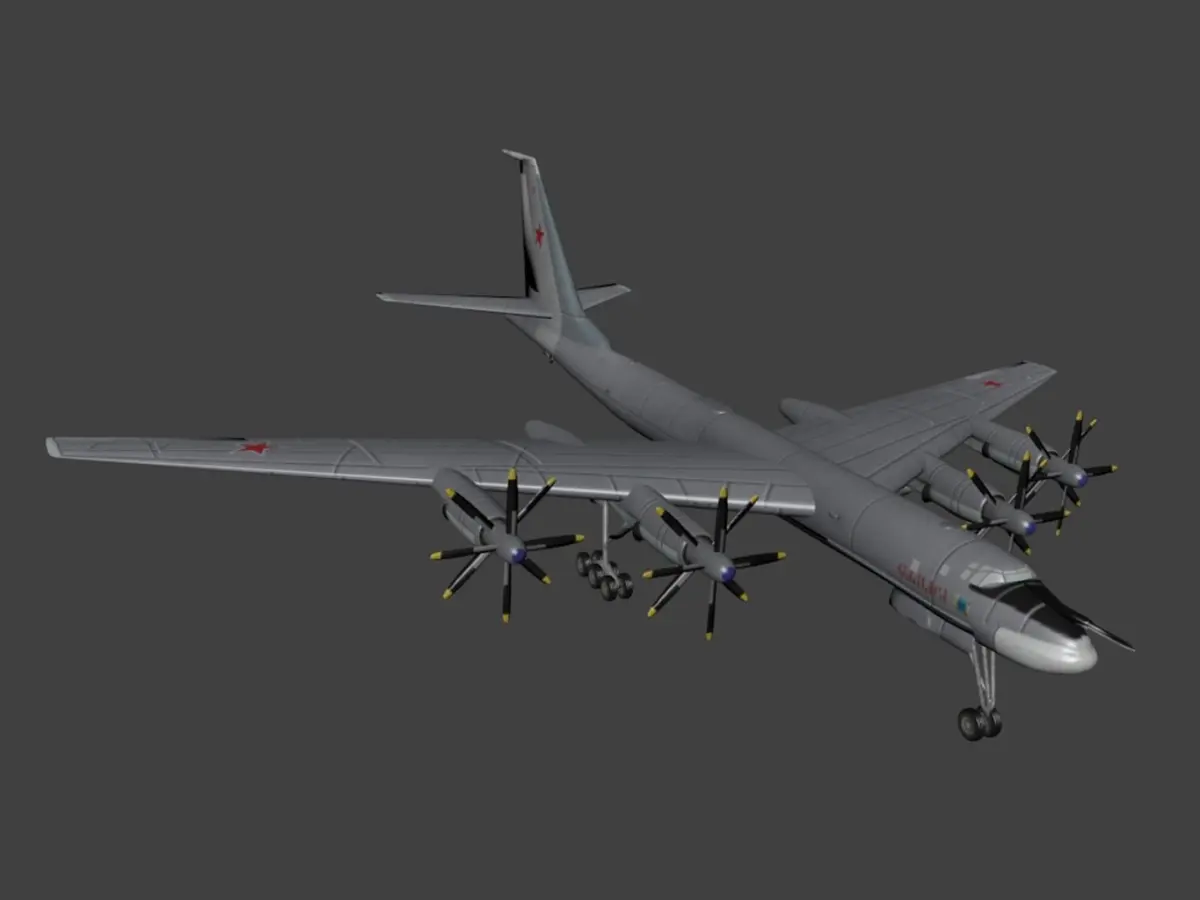
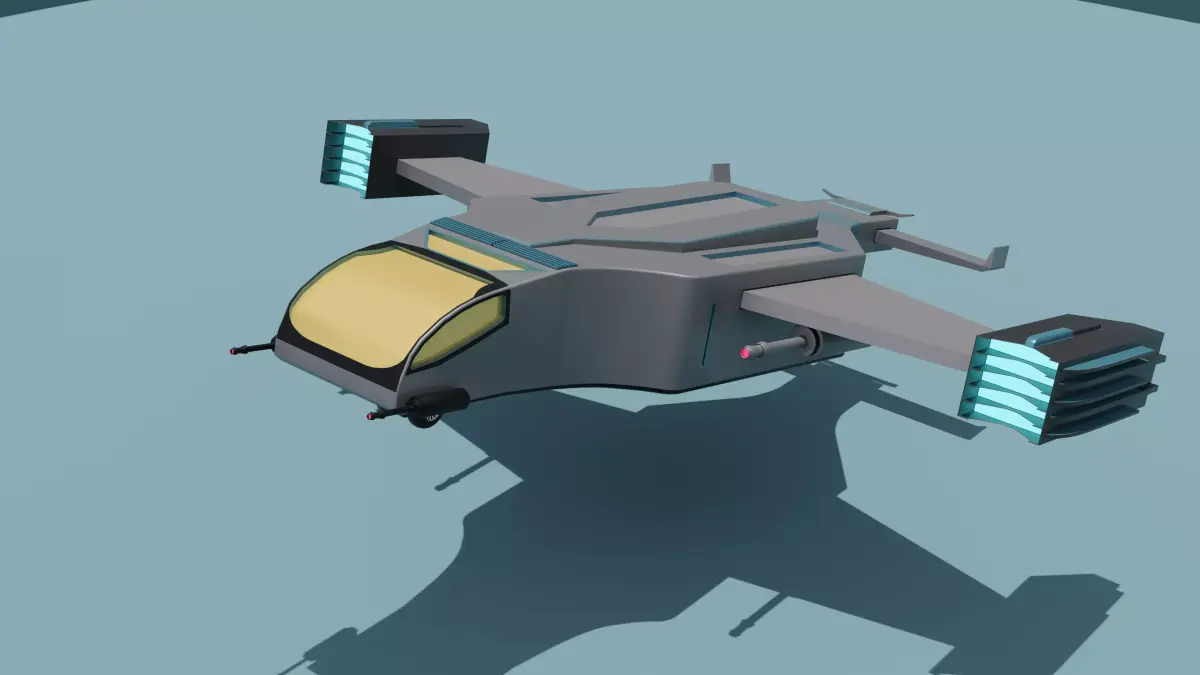
High-quality 3D assets at affordable prices — trusted by designers, engineers, and creators worldwide. Made with care to be versatile, accessible, and ready for your pipeline.
Included File Formats
This model is provided in 14 widely supported formats, ensuring maximum compatibility:
• - FBX (.fbx) – Standard format for most 3D software and pipelines
• - OBJ + MTL (.obj, .mtl) – Wavefront format, widely used and compatible
• - STL (.stl) – Exported mesh geometry; may be suitable for 3D printing with adjustments
• - STEP (.step, .stp) – CAD format using NURBS surfaces
• - IGES (.iges, .igs) – Common format for CAD/CAM and engineering workflows (NURBS)
• - SAT (.sat) – ACIS solid model format (NURBS)
• - DAE (.dae) – Collada format for 3D applications and animations
• - glTF (.glb) – Modern, lightweight format for web, AR, and real-time engines
• - 3DS (.3ds) – Legacy format with broad software support
• - 3ds Max (.max) – Provided for 3ds Max users
• - Blender (.blend) – Provided for Blender users
• - SketchUp (.skp) – Compatible with all SketchUp versions
• - AutoCAD (.dwg) – Suitable for technical and architectural workflows
• - Rhino (.3dm) – Provided for Rhino users
Model Info
• - All files are checked and tested for integrity and correct content
• - Geometry uses real-world scale; model resolution varies depending on the product (high or low poly)
• • - Scene setup and mesh structure may vary depending on model complexity
• - Rendered using Luxion KeyShot
• - Affordable price with professional detailing
Buy with confidence. Quality and compatibility guaranteed.
If you have any questions about the file formats, feel free to send us a message — we're happy to assist you!
Sincerely,
SURF3D
Trusted source for professional and affordable 3D models.
More Information About 3D Model :
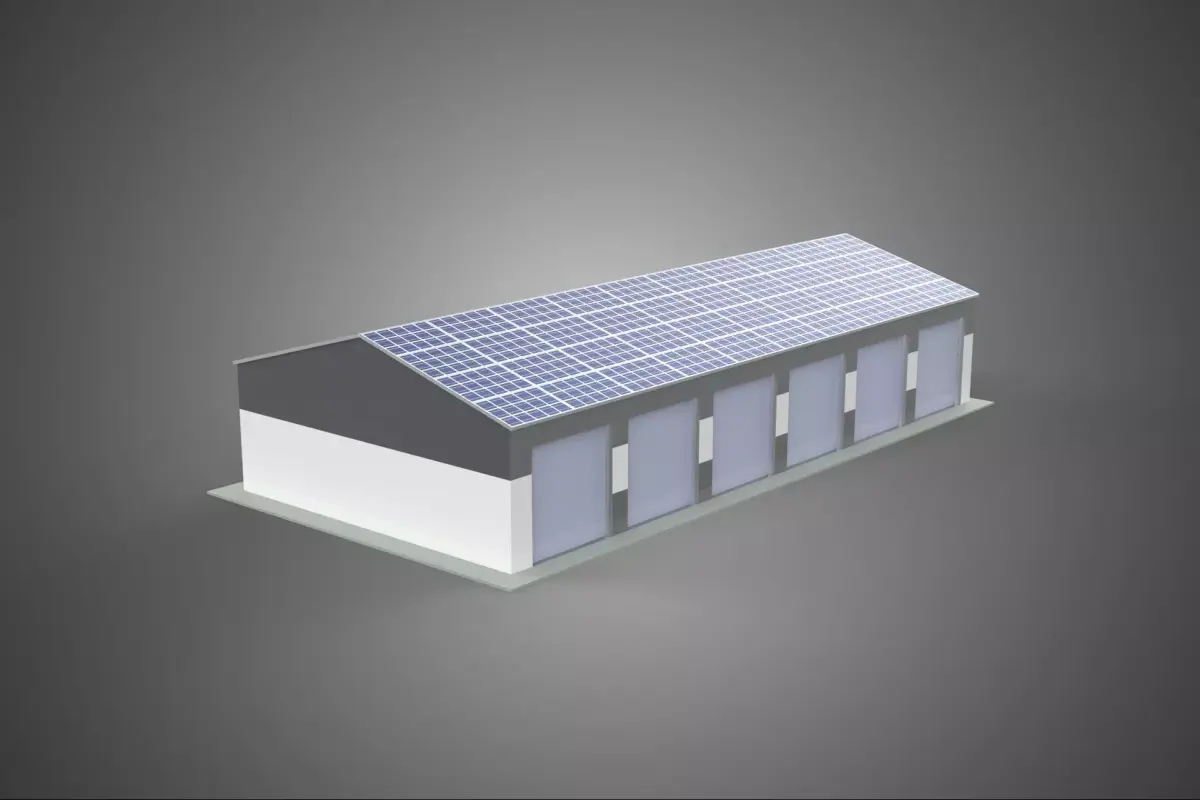
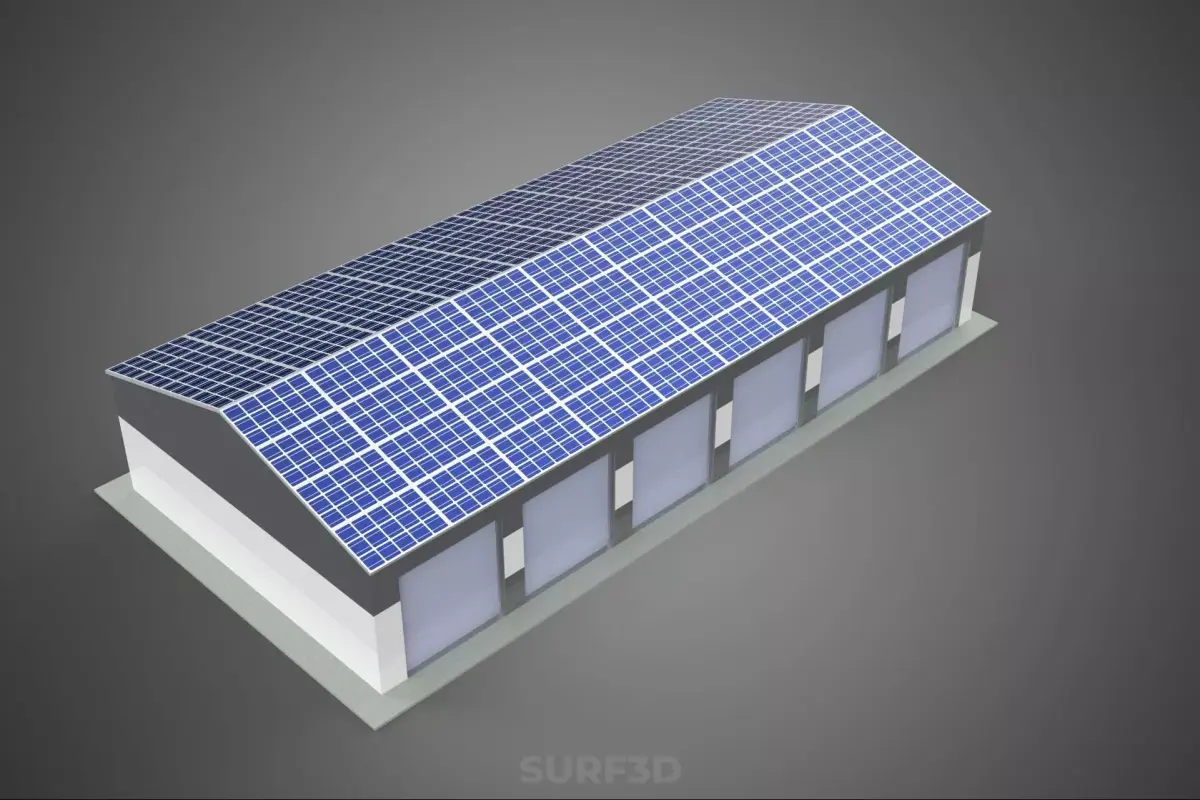
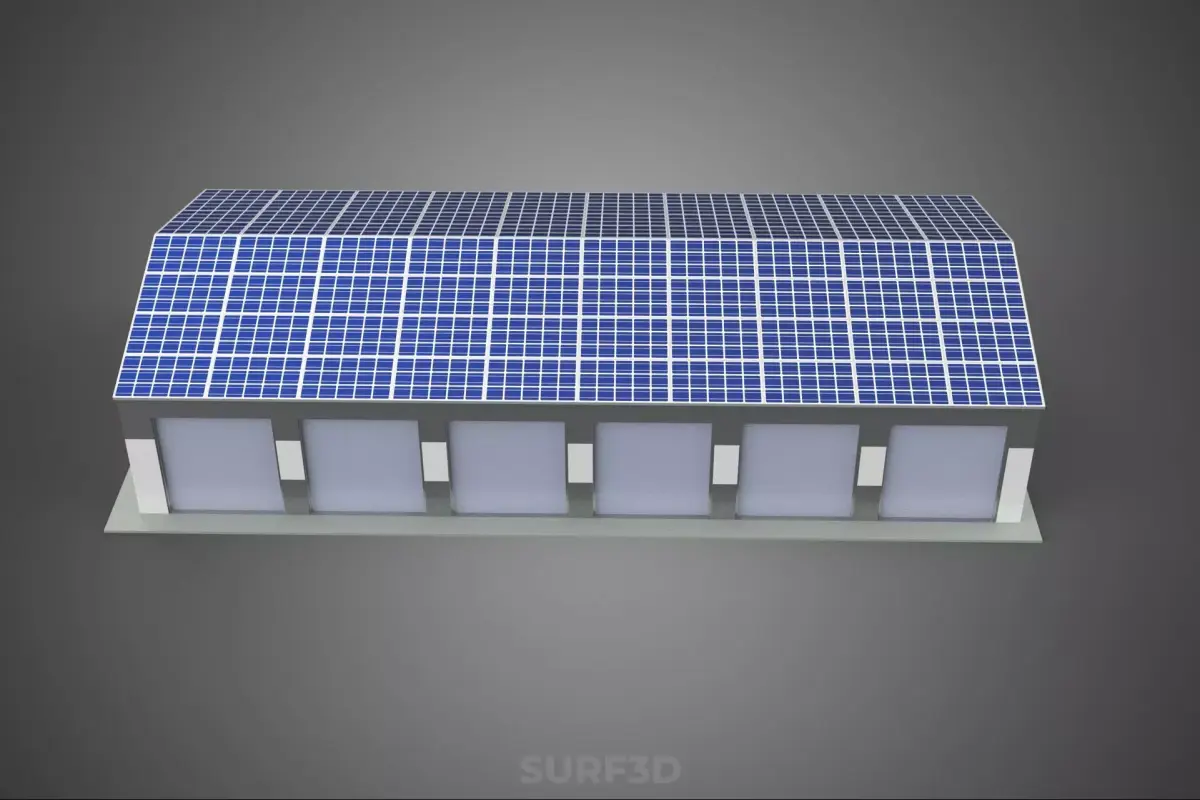
COMMERCIAL GARAGE BUILDING VEHICLE PARKING STORAGE SOLAR ENERGY
A Commercial Garage Building optimized for Vehicle Parking and Storage, integrating Solar Energy infrastructure (CGBVPSS), represents a specialized architectural and engineering typology designed to fulfill high-density vehicular accommodation requirements while simultaneously serving as a decentralized energy generation facility. These structures are fundamentally differentiated from conventional parking facilities through their emphasis on sustainable operation, reduced carbon footprint, and enhanced functional integration of renewable power systems.
Architectural and Structural Typology
CGBVPSS structures are predominantly multi-story, open-air or partially enclosed facilities, often utilizing reinforced concrete (post-tensioned or pre-cast systems) or structural steel framing to maximize clear-span capabilities and vehicle maneuverability. The design adheres to stringent building codes concerning fire suppression (e.g., NFPA 13), ventilation, seismic resilience, and accessibility (ADA compliance).
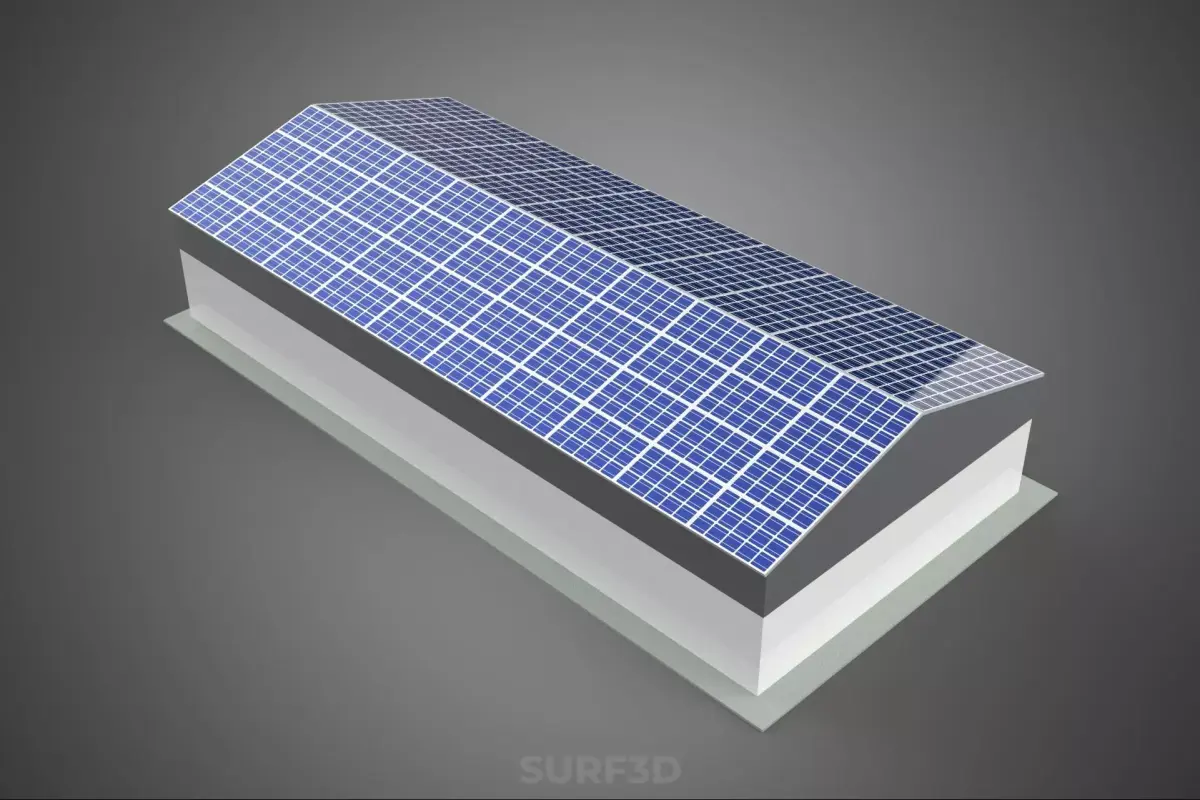
The critical architectural adaptation is the integration of solar arrays, typically Photovoltaic (PV) systems, mounted across the entire available horizontal surface area. This includes the roof deck and, increasingly, elevated canopy structures or awnings integrated into the upper parking levels or surrounding areas. Structural loading calculations must account for the additional dead load of the PV racking, panels, and associated balance-of-system (BOS) components, as well as dynamic loads such as wind uplift and snow accumulation, which are often amplified by the aerodynamic profile of the arrays.
Vehicle Parking and Storage Functionality
The primary function remains the efficient and secure storage of vehicles, ranging from standard passenger cars to commercial fleets. Design parameters focus on optimizing parking stall dimensions, ramp gradients, lane widths, and traffic flow patterns. Technology integration includes automated parking guidance systems (PGS), license plate recognition (LPR) for access control, and dedicated infrastructure for Electric Vehicle (EV) charging stations. The latter necessitates substantial electrical service capacity and robust conduit infrastructure, often leveraging the same electrical connection points and grid interconnection pathways established for the solar energy system. Security measures often include comprehensive CCTV surveillance and controlled entry/exit points.
Solar Energy Integration and Optimization
The integration of solar energy transforms the facility from a pure consumer of utilities into a potential net-zero or energy-positive operation.
1. Photovoltaic Systems
The most common application utilizes crystalline silicon PV panels (monocrystalline or polycrystalline). Arrays are generally mounted using non-penetrating ballasted racking systems or structural mounting systems integrated directly into the roof membrane. Optimal tilt and azimuth orientation are determined by the geographic location and facility aesthetics, often favoring a flat or slightly pitched installation to maximize parking space utilization beneath the array.
2. Energy Utilization and Grid Interconnection
The generated electricity serves multiple purposes:
- On-site Consumption: Powering internal systems, including lighting (predominantly high-efficiency LED fixtures controlled by occupancy sensors), elevators, ventilation, security systems, and EV charging infrastructure.
- Grid Export: Excess energy is exported to the utility grid under Net Metering or Power Purchase Agreement (PPA) structures, providing a revenue stream or offsetting peak demand charges.
- Energy Storage: Increasingly, Battery Energy Storage Systems (BESS) are integrated to store excess generation, manage demand charges (peak shaving), and provide resiliency, especially when supporting EV charging during high-utilization periods.
#### 3. Canopy Structures and Shade Integration
In many modern CGBVPSS designs, the solar arrays are elevated on purpose-built canopies spanning the top level. This configuration provides the dual benefit of generating energy and offering crucial weather protection (shade and precipitation shielding) to parked vehicles, enhancing the amenity value of the top deck. These solar carport structures require specialized structural engineering to manage height requirements and cantilevered loads.
### Sustainability and Economic Rationale
The economic viability of CGBVPSS derives from several factors. The initial capital investment for solar infrastructure is offset by reduced operational energy costs, potential energy sales, and eligibility for various governmental incentives (e.g., Investment Tax Credits, Renewable Energy Credits). Environmentally, the structure contributes significantly to urban sustainability goals by utilizing existing impervious surfaces (the parking structure footprint) for power generation, avoiding land use conflicts associated with ground-mounted solar farms, and facilitating the transition to electric mobility through integrated charging infrastructure.
***
KEYWORDS: Commercial Garage, Vehicle Parking, Storage Facility, Solar Energy, Photovoltaic System, Renewable Energy, Sustainable Architecture, Multi-Story Parking, EV Charging Infrastructure, Energy Storage, Net Metering, Structural Engineering, Reinforced Concrete, Building Code Compliance, Grid Interconnection, Distributed Generation, Energy Efficiency, Demand Management, Solar Carport, Canopy Structure, LEED Certification, Urban Planning, Asset Utilization, Infrastructure Development, Automated Parking, Access Control, Security Systems, Post-Tensioned Structure, Life Cycle Assessment, Carbon Reduction.