- Description
- Formats
Description
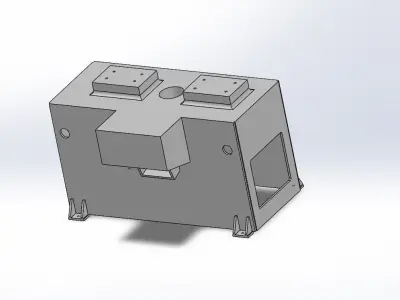
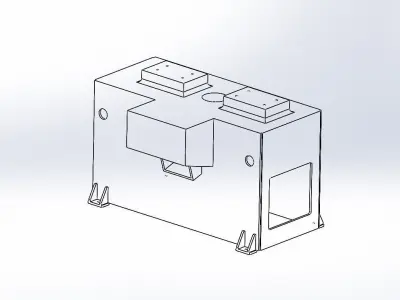
Designing a 3D work table in SolidWorks involves several considerations to ensure it meets functional requirements and is manufacturable. Here are some key factors to consider:
- Purpose and RequirementsUse Case: Determine the primary use of the work table (e.g., assembly, machining, general work).Load Capacity: Estimate the maximum weight the table needs to support.Dimensions: Define the length, width, and height based on available space and user comfort.Features: Consider features like adjustable height, built-in storage, or integrated workstations.
- Material SelectionStrength and Durability: Choose materials that can handle the expected loads and wear. Common materials include steel for strength, aluminum for lightweight properties, or wood for versatility.Cost: Balance between material cost and performance.Manufacturability: Consider how the materials will be processed and joined (welding, bolting, etc.).
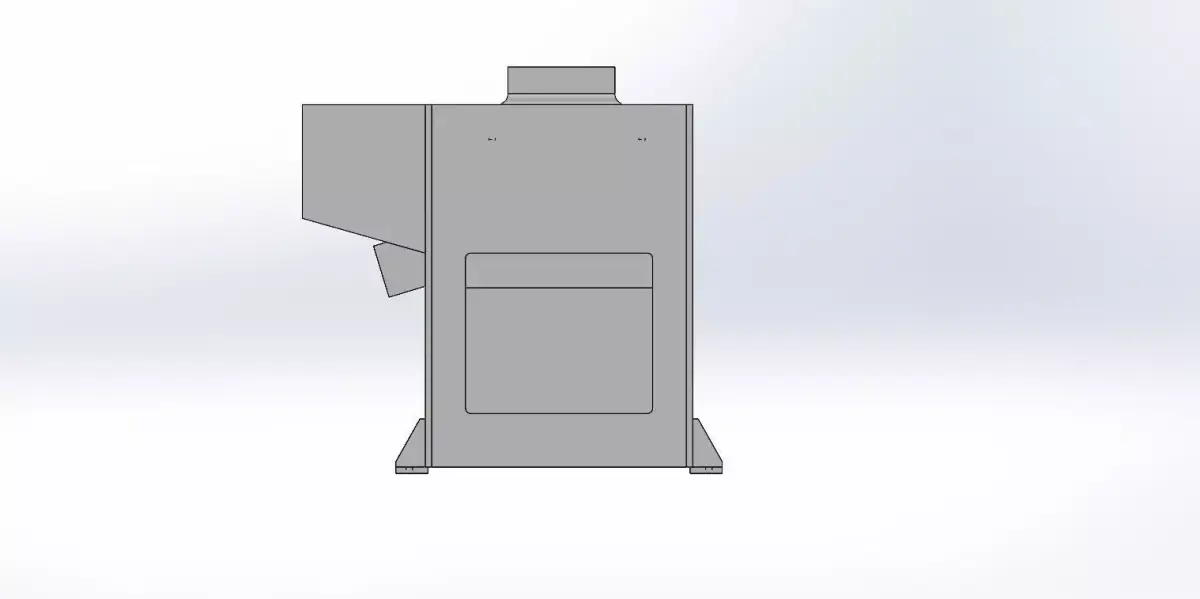
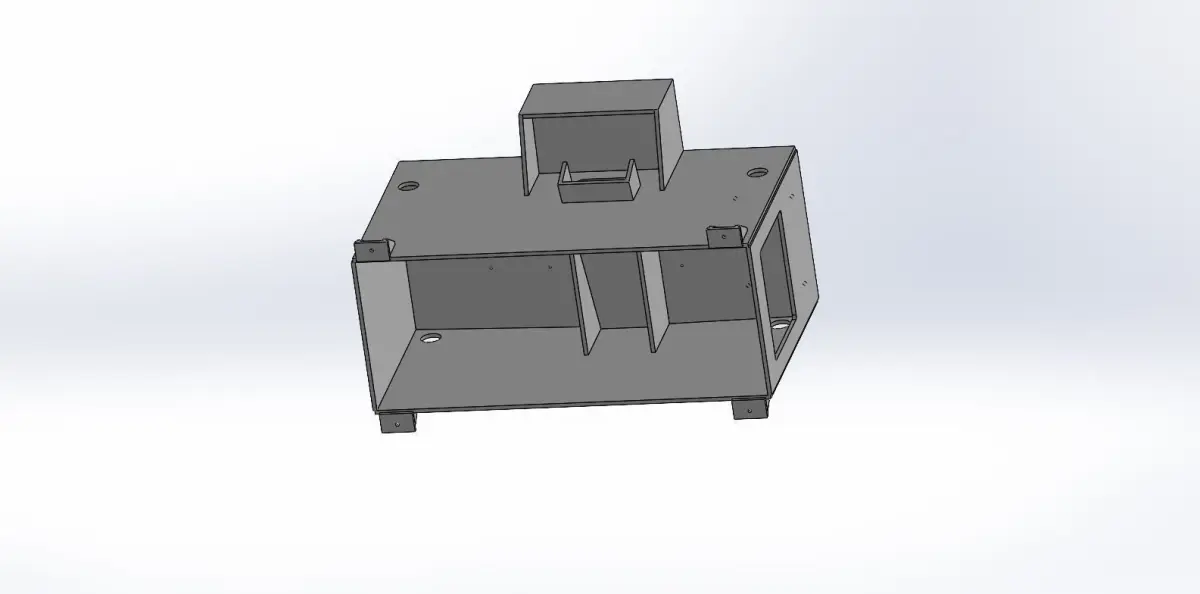
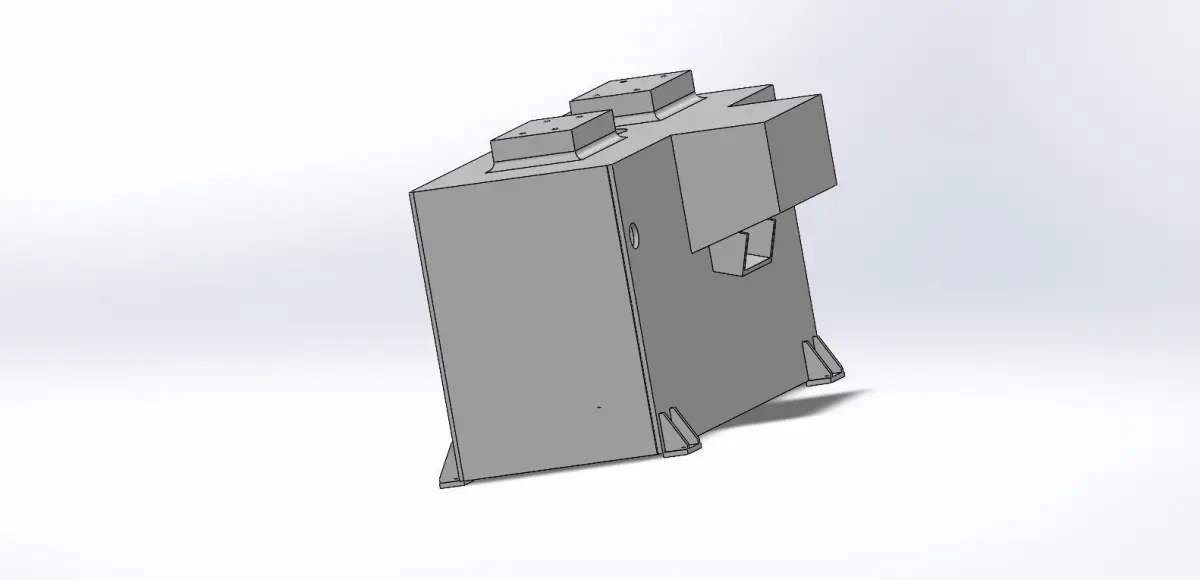
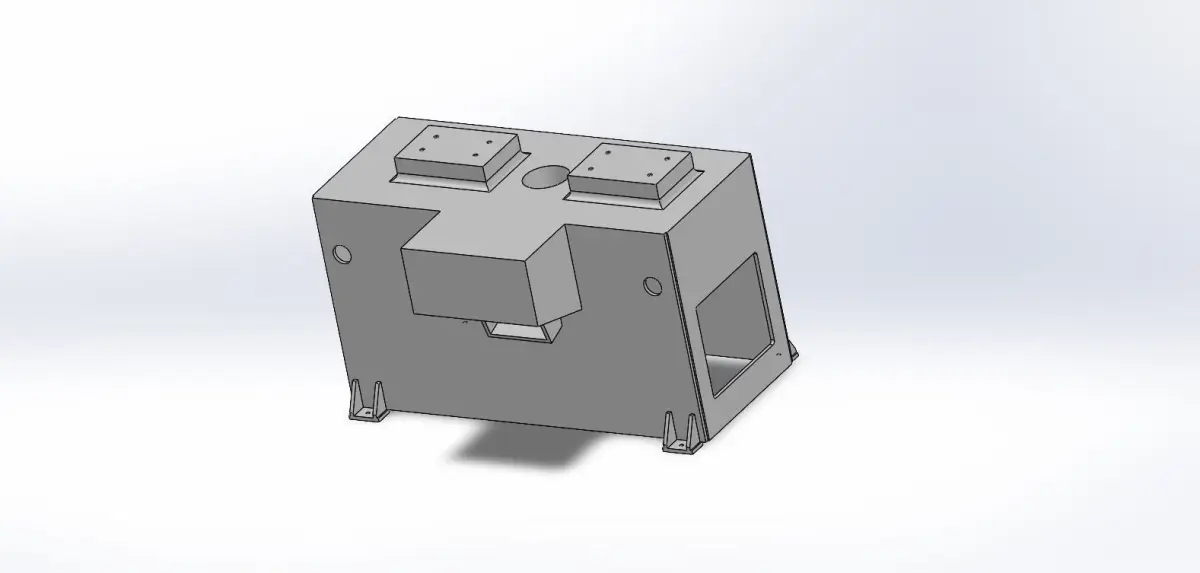
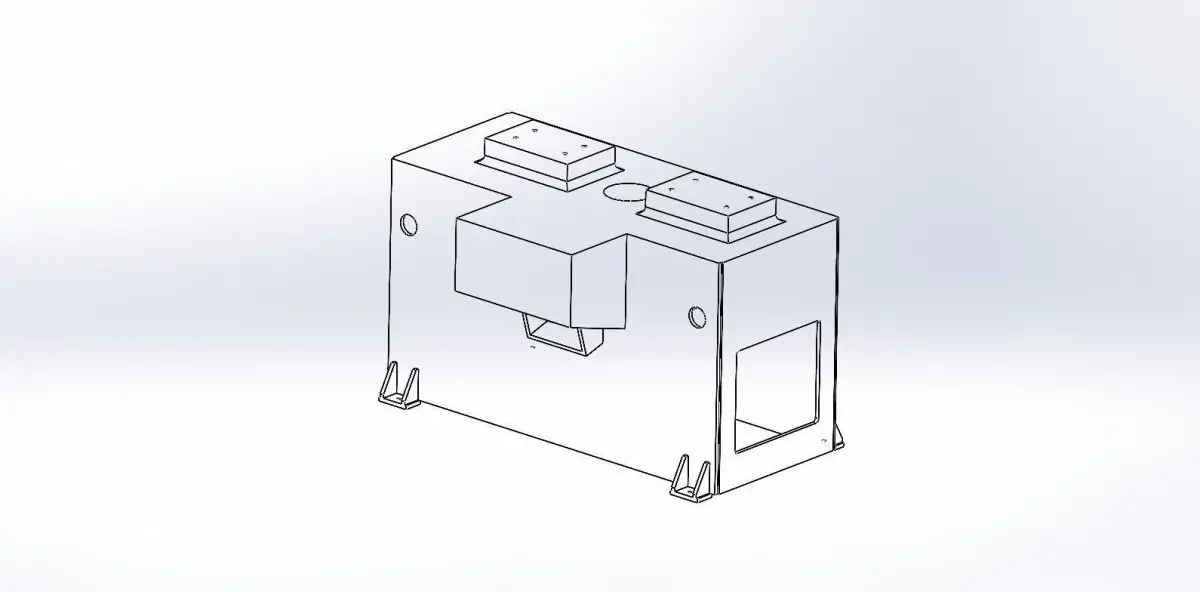
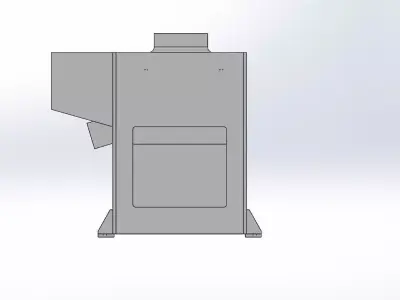
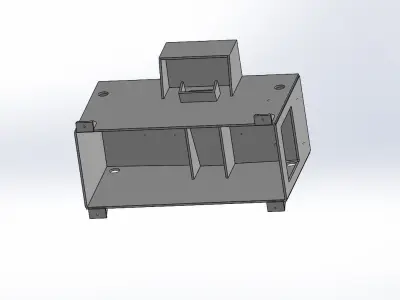
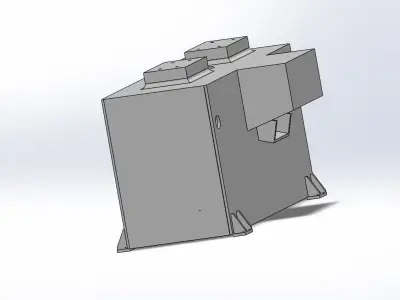
- Structural DesignFrame: Design a robust frame that provides stability and can support the tabletop and additional components.Legs: Ensure the legs are designed to handle the load and provide stability. Consider features like adjustable feet for uneven floors.Tabletop: Ensure it’s strong enough for the intended use. For instance, a workbench might require a thicker, reinforced tabletop.
- ErgonomicsHeight: Design the table height to be comfortable for users. Adjustable height can be beneficial for various tasks.Accessibility: Ensure that the table’s design allows easy access to all parts, especially if it includes built-in storage or tools.
- Modularity and FlexibilityCustomizability: Incorporate features that allow for future modifications or additions, such as modular components or adjustable fixtures.Expandability: Design the table so that additional features or accessories can be added later.
- Assembly and ManufacturingJoinery: Decide on methods for joining parts (welding, bolts, screws) and ensure they are easy to assemble and disassemble if needed.Tolerance and Fit: Ensure parts fit together correctly with appropriate tolerances.Manufacturing Processes: Account for the processes involved in making each part, such as cutting, machining, and finishing.
- Safety ConsiderationsStability: Ensure the table is stable and won’t tip over easily, especially under load.Sharp Edges: Avoid sharp edges and corners that could cause injury.Load Distribution: Design the structure to distribute loads evenly to avoid excessive stress on any single part.
- Aesthetics and FinishAppearance: Design the table to match its intended environment, whether it’s a professional workshop or a home garage.Surface Finish: Consider coatings or finishes that protect the table from corrosion and wear, and are easy to clean.
- Software Considerations in SolidWorksAssemblies: Use SolidWorks assemblies to test the fit and function of the table’s components.Simulation: Utilize SolidWorks Simulation to analyze stress, strain, and deformation to ensure the design can handle expected loads.Drafting: Generate detailed drawings and parts lists to assist in manufacturing and assembly.
- Compliance and StandardsRegulations: Ensure the design meets any relevant standards or regulations for safety and quality.Industry Standards: Follow best practices and industry standards for similar types of work tables.Design Workflow in SolidWorksSketching: Start with 2D sketches for base profiles and critical features.Extrusions and Cutouts: Create 3D models using extrusions, cutouts, and other features.Assembly: Assemble individual parts to check fit and functionality.Simulation: Run simulations to validate strength and performance.Drawings: Generate detailed engineering drawings for manufacturing.By addressing these considerations, you’ll be able to create a functional and efficient 3D work table design in SolidWorks.
Features
- Animated
- Rigged
- Ready for 3D Printing
- VR / AR / Low-poly
- PBR
- Textures
- Materials
- UV Mapping
- Unwrapped UVs: Unknown
- Geometry: -
- Polygons: 0
- Vertices: 0
- Plugins used
All content related to this 3D asset—including renders, descriptions, and metadata—is
credited to its original author, «softappsun». CGhub does not claim copyright ownership over the content used.
credited to its original author, «softappsun». CGhub does not claim copyright ownership over the content used.
- SolidWorks 2021 ()685 KBVersion: 2021Renderer: Mental Ray 2021