High-quality 3D assets at affordable prices — trusted by designers, engineers, and creators worldwide. Made with care to be versatile, accessible, and ready for your pipeline.
Included File Formats
This model is provided in 14 widely supported formats, ensuring maximum compatibility:
• - FBX (.fbx) – Standard format for most 3D software and pipelines
• - OBJ + MTL (.obj, .mtl) – Wavefront format, widely used and compatible
• - STL (.stl) – Exported mesh geometry; may be suitable for 3D printing with adjustments
• - STEP (.step, .stp) – CAD format using NURBS surfaces
• - IGES (.iges, .igs) – Common format for CAD/CAM and engineering workflows (NURBS)
• - SAT (.sat) – ACIS solid model format (NURBS)
• - DAE (.dae) – Collada format for 3D applications and animations
• - glTF (.glb) – Modern, lightweight format for web, AR, and real-time engines
• - 3DS (.3ds) – Legacy format with broad software support
• - 3ds Max (.max) – Provided for 3ds Max users
• - Blender (.blend) – Provided for Blender users
• - SketchUp (.skp) – Compatible with all SketchUp versions
• - AutoCAD (.dwg) – Suitable for technical and architectural workflows
• - Rhino (.3dm) – Provided for Rhino users
Model Info
• - All files are checked and tested for integrity and correct content
• - Geometry uses real-world scale; model resolution varies depending on the product (high or low poly)
• • - Scene setup and mesh structure may vary depending on model complexity
• - Rendered using Luxion KeyShot
• - Affordable price with professional detailing
Buy with confidence. Quality and compatibility guaranteed.
If you have any questions about the file formats, feel free to send us a message — we're happy to assist you!
Sincerely,
SURF3D
Trusted source for professional and affordable 3D models.
More Information About 3D Model :
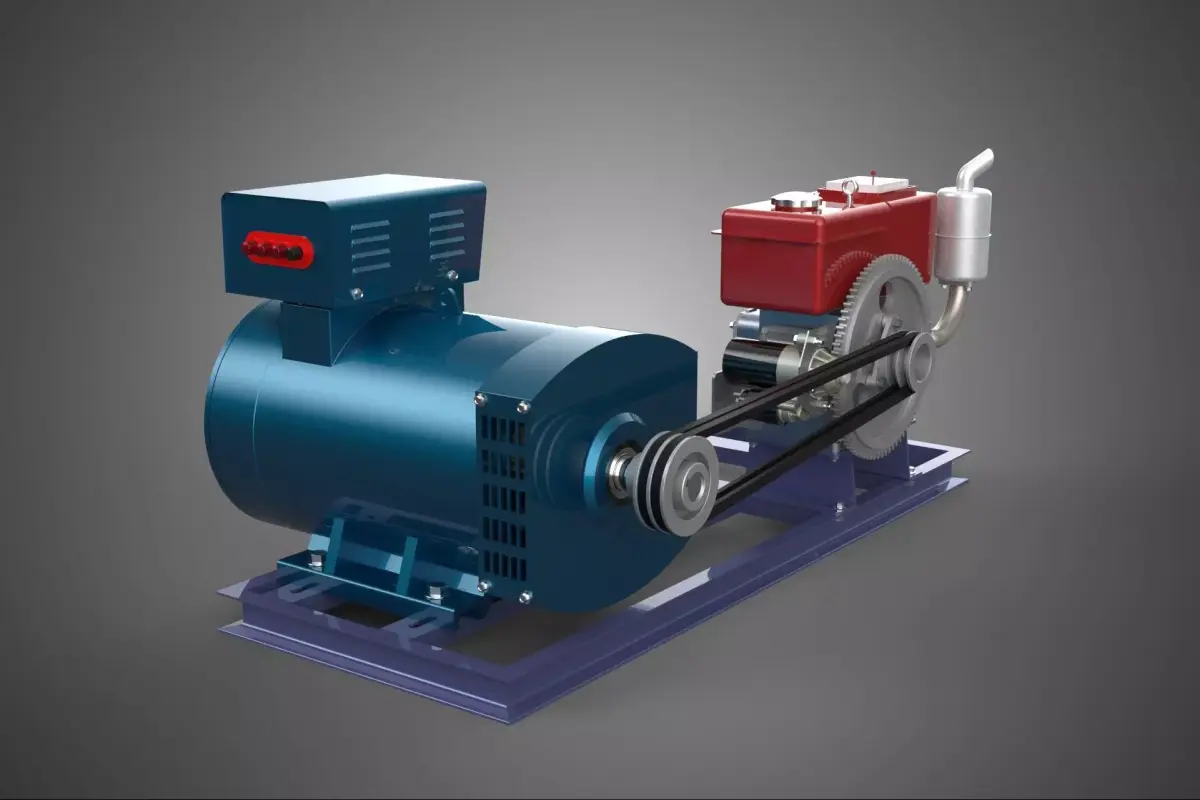
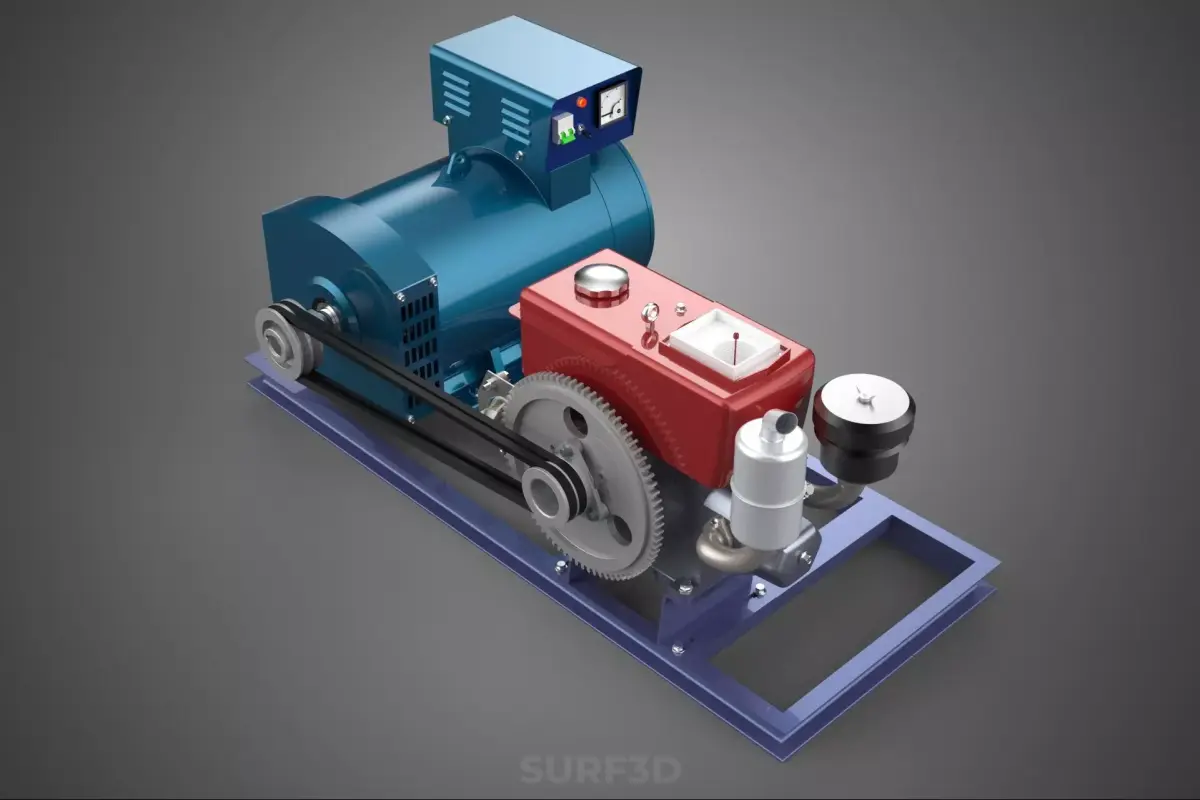
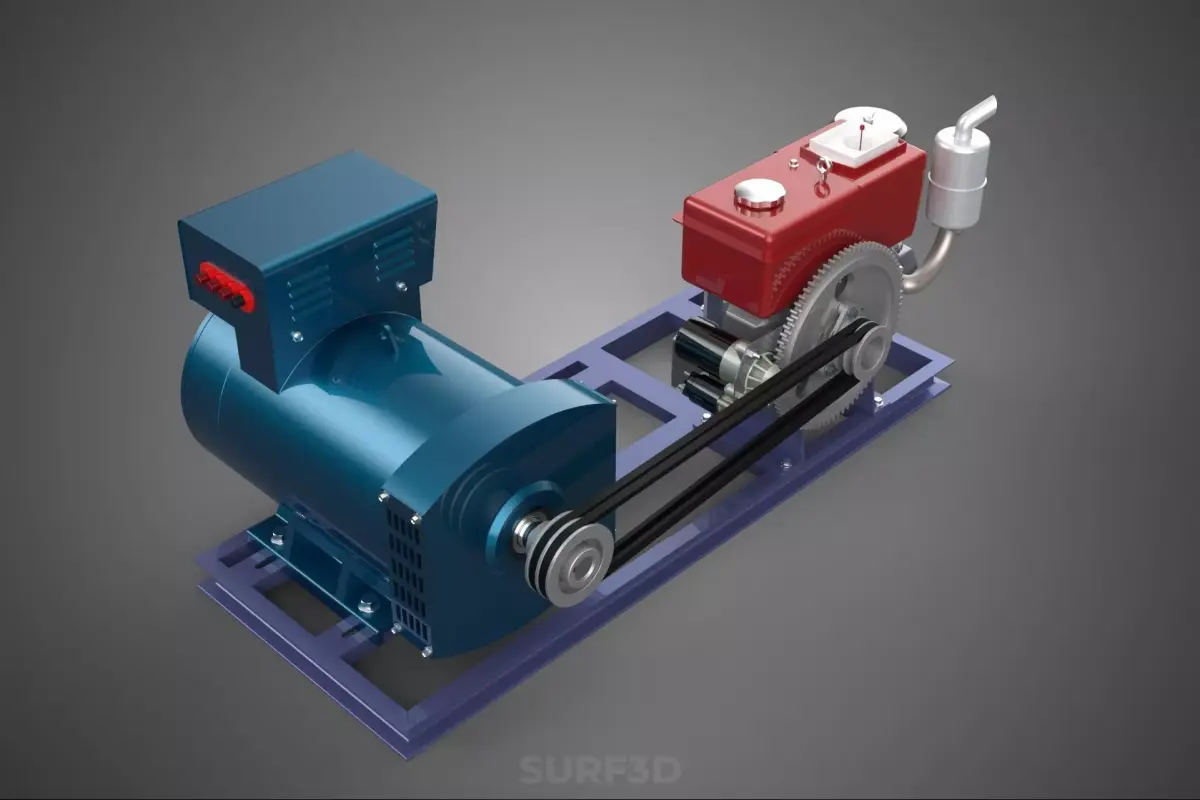
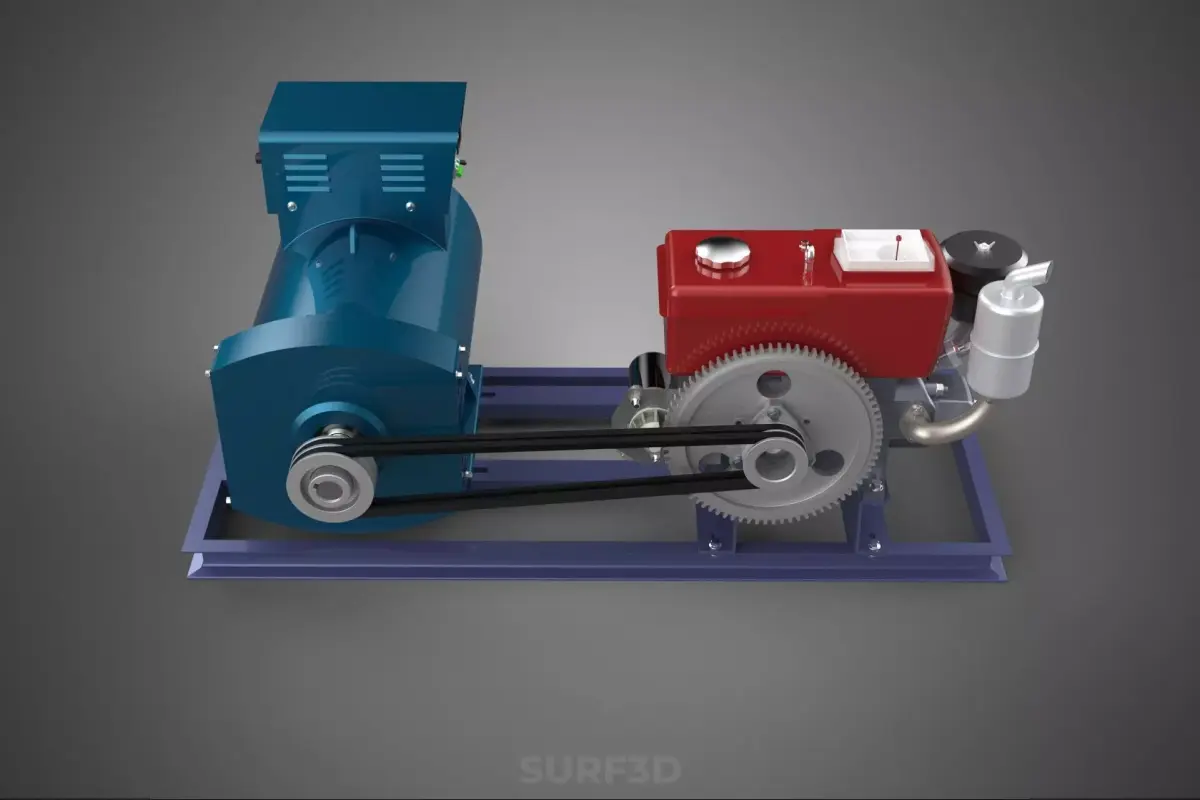
A Diesel Generator Set, commonly referred to by the portmanteau genset, is a sophisticated, integrated mechanical system that functions as a self-contained unit for generating electrical power. The assembly comprises a diesel engine (the prime mover) mechanically coupled to an electrical generator (alternator or dynamo). This apparatus converts the chemical energy stored in diesel fuel into mechanical rotational energy, which is subsequently transformed into usable electrical energy through the principle of electromagnetic induction.
Nomenclature and Core Components
The terminology associated with the system reflects its dual nature. The Diesel Engine serves as the prime mover, operating on the compression-ignition cycle popularized by Rudolf Diesel. It provides the necessary rotational force (torque) at a precise angular velocity to maintain the required electrical frequency (e.g., 50 Hz or 60 Hz).
The electrical component is typically an Alternator, a type of synchronous generator designed to produce alternating current (AC). Historically, the term Dynamo referred specifically to a direct current (DC) generator, and while some specialty sets may use DC output, modern power generation overwhelmingly utilizes alternators. The inclusion of the term Motor in generalized titles is often used colloquially for rotating electrical machinery, though a motor technically performs the reverse operation—converting electrical energy into mechanical energy.
The engine and alternator are mounted onto a common skid or base frame, often with vibration isolators to minimize mechanical stress and noise transmission. Critical ancillary systems supporting the operation include:
- Fuel System: Storage tank, filters, and injectors ensuring precise fuel delivery.
- Cooling System: Utilizing radiator fluid or air to dissipate the significant waste heat generated by the engine.
- Lubrication System: Oil sump, pumps, and filters to minimize friction and wear.
- Control Panel (Switchgear): The central nervous system, housing automatic voltage regulators (AVR), frequency monitoring, protective relays, and automatic transfer switch (ATS) functionality for standby applications.
### Operational Principles
The process begins when the diesel engine combusts fuel through compression ignition, driving the crankshaft. This rotation is transferred directly to the rotor of the alternator. The rotor, containing magnetic field windings excited by a small DC current, rotates within the stationary windings of the stator. The continuous cutting of magnetic flux lines by the stator windings induces electromotive force (EMF), resulting in the generation of alternating electrical current, governed by Faraday's Law of Induction.
Diesel gensets are favored in industrial contexts due to the high thermal efficiency of the compression-ignition cycle, which translates to superior fuel economy, particularly under heavy load conditions, and their robust torque delivery characteristics.
### Applications and Classification
Diesel gensets are classified based on their output capacity (ranging from a few kilowatts (kW) to several megawatts (MW)) and their intended duty cycle:
- Standby/Emergency Power: These units remain inactive but ready to deploy instantly (via the ATS) upon detection of a utility grid failure. They are essential for critical infrastructure such as hospitals, data centers, airports, and telecommunications hubs, ensuring business continuity and life safety.
- Prime Power: Used in locations where connection to the public utility grid is non-existent or impractical (e.g., remote mining camps, construction sites, or isolated military bases). They operate continuously as the primary source of electricity.
- Peaking/Load Management: Large industrial units used to supplement the grid supply during periods of high electrical demand (peak shaving), thereby reducing reliance on potentially more expensive utility power rates.
Modern gensets incorporate sophisticated electronic controls for monitoring performance parameters, ensuring stable output frequency and voltage regulation crucial for protecting sensitive electrical equipment.
KEYWORDS: Diesel Engine, Generator Set, Genset, Alternator, Prime Mover, Power Generation, Standby Power, Emergency Power, Continuous Power, Compression Ignition, Kilowatt, Megawatt, Fuel Efficiency, Voltage Regulation, Frequency Control, Control Panel, Internal Combustion, Prime Power, Peaking Unit, Rotating Machinery, Stator, Rotor, Electromagnetic Induction, Power Factor, Cooling System, Industrial Power, Data Center Backup, Load Shedding, Switchgear, Synchronous Generator